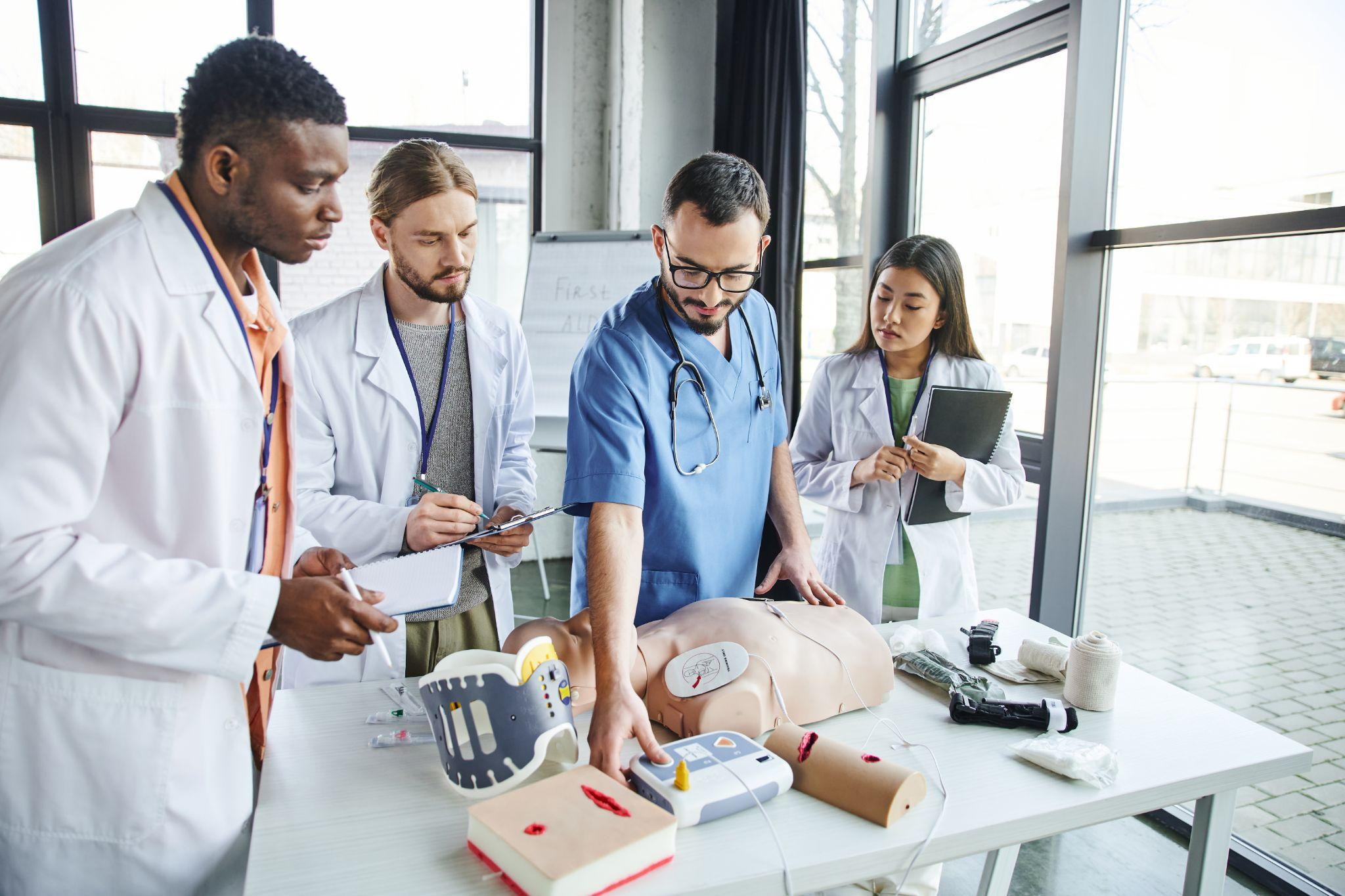
The American Heart Association (AHA) has released the highly anticipated 2025 updates to the Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) guidelines. These evidence-based recommendations serve as a crucial resource for healthcare professionals, guiding their management of patients experiencing cardiac arrest and other life-threatening cardiovascular emergencies.
The 2025 ACLS guidelines incorporate the latest research findings and expert consensus to optimize patient care and outcomes. The updates focus on several key areas, including high-quality CPR techniques, advanced airway management, defibrillation strategies, medication administration, and post-cardiac arrest care.
By staying current with these guidelines, medical professionals can ensure they are providing the most effective and up-to-date treatment to their patients in critical situations. The 2025 ACLS updates emphasize the importance of a well-coordinated, team-based approach to resuscitation efforts, with a strong focus on communication and continuous quality improvement.
Overview of the 2025 ACLS Guideline Updates
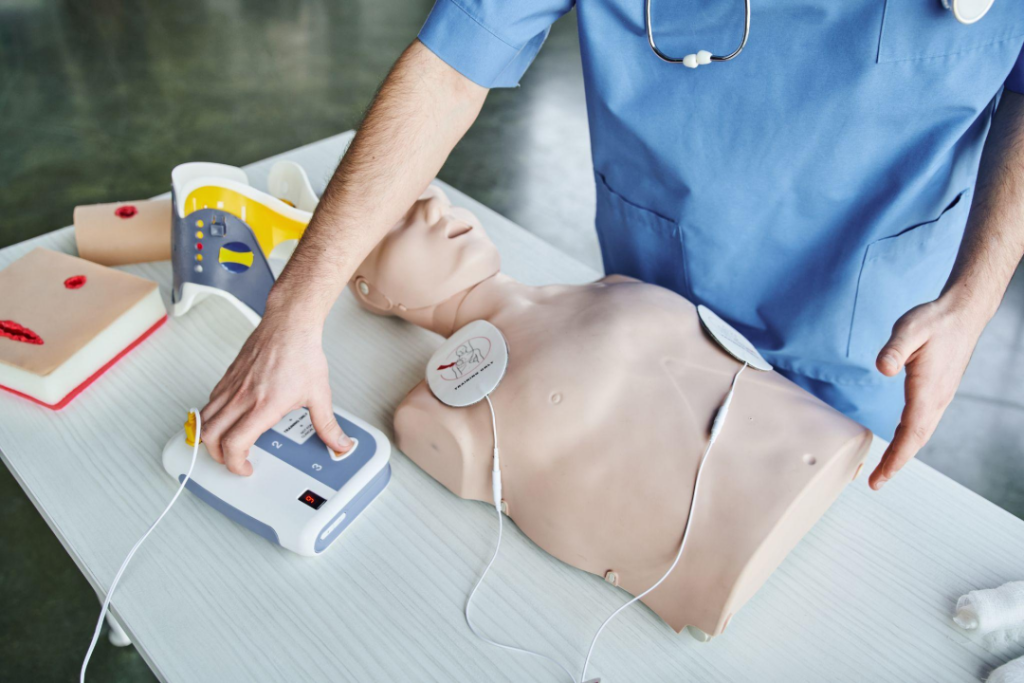
The 2025 ACLS guidelines incorporate the latest evidence-based recommendations for managing patients with cardiac arrest and other cardiovascular emergencies. These updates are the result of a rigorous review process conducted by experts in the field, ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to the most current and reliable information, such as the American College of Cardiology guidelines and resources, to guide their practice.
Key changes in the 2025 guidelines include:
- CPR Techniques: Emphasis on high-quality CPR with a chest compression rate of 100-120 per minute and a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) for adults, while allowing full chest recoil and minimizing interruptions.
- Medication Administration: Updates to the timing and dosage of epinephrine administration during cardiac arrest, as well as recommendations for considering amiodarone or lidocaine for refractory ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care: Recommendations for targeted temperature management in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest, maintaining blood glucose levels between 144-180 mg/dL (8-10 mmol/L), and performing early coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for patients with suspected cardiac etiology of arrest.
The guidelines stress the importance of a systematic approach to identifying and treating reversible causes of cardiac arrest, known as the “H’s and T’s.” This includes using point-of-care ultrasound to diagnose treatable conditions such as cardiac tamponade, pulmonary embolism, or hypovolemia, and administering thrombolytics for suspected or confirmed pulmonary embolism causing cardiac arrest.
Moreover, the 2025 ACLS guidelines highlight the value of physiologic monitoring during CPR, such as using end-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) monitoring to assess CPR quality and detect return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), and considering arterial pressure monitoring to optimize chest compression quality and guide vasopressor therapy.
By familiarizing themselves with these updated guidelines, healthcare professionals can provide the highest standard of care to their patients, ultimately improving survival rates and neurological outcomes following cardiac arrest. The 2025 ACLS updates serve as a vital tool for medical professionals seeking to enhance their knowledge and skills in managing these critical situations, such as those obtaining ACLS certification through trusted providers like Affordable ACLS.
High-Quality CPR Remains the Foundation of ACLS
The effectiveness of Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support hinges on the delivery of proficient CPR. Focus on a compression rhythm that mirrors the natural heartbeat, maintaining a steady rate that supports circulation to vital organs. Precision in achieving the recommended depth during compressions is crucial, providing the necessary force to sustain cerebral and myocardial perfusion.
Ensuring that each compression is followed by complete chest recoil is vital—it facilitates venous return and aids in optimizing cardiac output. The continuity of compressions without unnecessary pauses is paramount; quick and seamless transitions during interventions are essential to maintaining blood flow.
Ventilation must be approached with care to avoid over-inflation, which can impede venous return and reduce cardiac efficiency. Precision in ventilation helps maintain optimal perfusion pressures, thus supporting patient recovery.
Updates in Airway Management During Cardiac Arrest
The 2025 ACLS guidelines introduce refined approaches to airway management that enhance the effectiveness of oxygenation and ventilation during resuscitation. Bag-mask ventilation remains a cornerstone for initial airway support, providing a straightforward method to deliver breaths quickly. Advanced airway options, such as endotracheal intubation and supraglottic devices, offer robust alternatives, particularly in extended resuscitation scenarios where maintaining a patent airway is crucial.
When an advanced airway is employed, adherence to precise ventilation timing is essential—administering 1 breath every 6 seconds allows for consistent oxygen delivery without disrupting the rhythm of chest compressions. This careful timing plays a pivotal role in ensuring that oxygenation remains effective throughout the resuscitation process.
To verify the correct placement of advanced airways, the guidelines emphasize the use of waveform capnography. This monitoring tool provides continuous feedback on the airway status and ventilation efficacy, complementing traditional clinical assessments. By integrating these practices, healthcare providers can optimize respiratory management during cardiac arrest, supporting improved patient outcomes.
Defibrillation Strategies for Shockable Rhythms
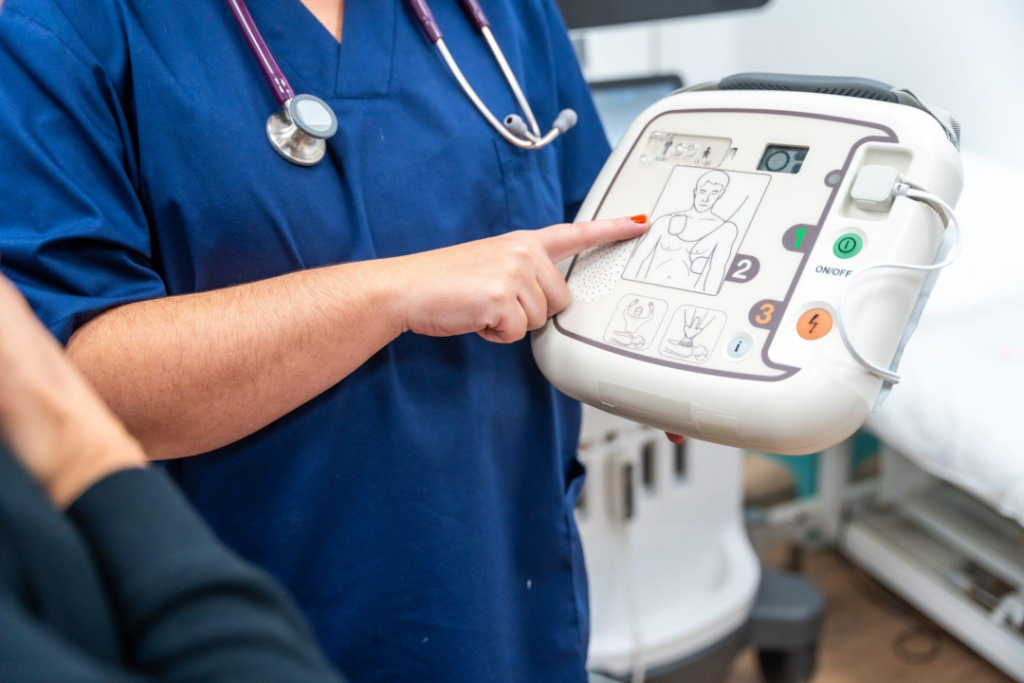
When encountering shockable rhythms such as ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT), decisive intervention plays a critical role. Immediate defibrillation is prioritized to rapidly restore an effective cardiac rhythm, with the goal of minimizing downtime and enhancing patient survival prospects. The updated guidelines emphasize reducing the interval to the first shock, as each second saved significantly impacts the chances of a successful resuscitation.
For cases where VF persists after initial attempts, the guidelines suggest exploring advanced defibrillation techniques. Double sequential defibrillation involves delivering two shocks in quick succession from separate defibrillators, offering a potential solution for cases resistant to standard interventions. This method, requiring precise coordination and preparation, provides an additional option for healthcare providers facing refractory VF.
Following defibrillation, it is essential to promptly resume high-quality CPR. This ensures continuous perfusion to vital organs, with rhythm checks conducted systematically every two minutes to guide further treatment. This structured approach reinforces the guidelines’ commitment to maintaining an efficient and responsive resuscitation process throughout the cardiac arrest event.
Medication Administration During Cardiac Arrest
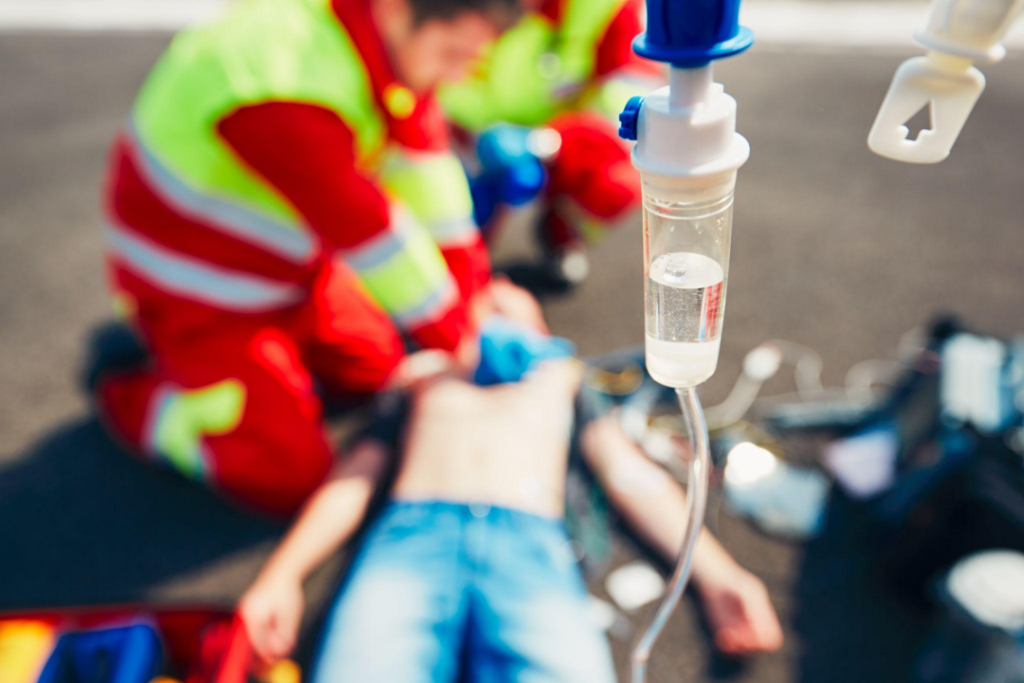
During cardiac arrest, the administration of medications plays a pivotal role in facilitating the resuscitation process. A key agent in this protocol is a vasopressor, administered to bolster coronary and cerebral perfusion by increasing systemic vascular resistance and improving myocardial contractility. This pharmacological support is crucial for maintaining perfusion during the resuscitation efforts.
For patients experiencing persistent ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, the guidelines recommend the incorporation of specific antiarrhythmic medications. Agents such as amiodarone and lidocaine are utilized for their capacity to suppress arrhythmias by stabilizing cardiac electrophysiology. Amiodarone is frequently employed in this setting, with lidocaine serving as an alternative, particularly beneficial when amiodarone is not available.
The guidelines advise against the routine use of certain adjunctive medications during cardiac arrest. Agents such as calcium, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium, and steroids are reserved for specific clinical indications due to a lack of evidence supporting their broad efficacy in improving outcomes. This targeted approach ensures that each pharmacological intervention is both deliberate and supported by clinical evidence, maximizing the potential for a successful resuscitation.
Identifying and Treating Reversible Causes
A crucial aspect of Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support involves swiftly addressing causes of cardiac arrest that can be reversed with targeted interventions. This approach requires healthcare professionals to systematically evaluate potential underlying issues, guided by standardized cardiac care performance measures, that can be corrected to restore cardiac function.
Utilizing diagnostic tools such as advanced imaging provides valuable insights into the patient’s physiological state. Techniques like echocardiography can assist in identifying conditions such as fluid accumulation around the heart, which may impede normal cardiac activity. Similarly, imaging can reveal obstructions in major blood vessels that could compromise circulation, aiding in the formulation of an effective treatment plan.
In cases where a blockage in the pulmonary artery is suspected, the administration of specific therapeutic agents can be lifesaving. These agents work to dissolve clots, thereby restoring normal blood flow to the lungs and improving overall cardiovascular stability. By integrating these diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, healthcare providers can address reversible conditions with precision, enhancing the likelihood of a successful resuscitation outcome.
Physiologic Monitoring During CPR
Incorporating advanced physiologic monitoring into resuscitation efforts elevates the precision of care during CPR. The use of capnography, particularly capnometric devices, provides critical real-time insights into the effectiveness of compressive efforts. By monitoring the carbon dioxide levels in exhaled air, clinicians gain a clear picture of perfusion status and respiratory efficacy. A sudden increase in these levels can indicate a return of spontaneous circulation, prompting a strategic reassessment of the resuscitation approach.
Arterial waveform analysis further complements this by offering continuous, real-time blood pressure data during CPR. This data is invaluable for fine-tuning the force and rate of compressions, as well as for making informed decisions about vasopressor administration. Such precision ensures that perfusion pressures are maintained at optimal levels, tailored to the physiological responses observed in each patient, thus maximizing the likelihood of recovery.
Ventilation management remains pivotal in maintaining physiological equilibrium during resuscitation. Monitoring respiratory parameters closely can prevent hyperventilation, which is associated with a decline in effective blood flow. By adjusting ventilation rates to maintain optimal carbon dioxide levels, resuscitation teams can ensure that their efforts support rather than compromise the patient’s physiological stability. This sophisticated approach reinforces the fundamental role of physiologic monitoring in delivering high-quality, evidence-based resuscitation care.
Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
Transitioning from resuscitation to post-cardiac arrest care necessitates a strategic focus on interventions that stabilize the patient and support optimal recovery. Temperature control is a critical component in this phase, designed to protect neurological function in patients who remain unresponsive after resuscitation. This involves precise management of the patient’s body temperature, leveraging advanced cooling methods to balance the potential benefits with the risks of adverse effects.
Metabolic equilibrium is equally important in post-resuscitation management. Monitoring and adjusting blood glucose levels within a specific range aids in maintaining cellular integrity and preventing further damage. This balanced approach addresses the dual concerns of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, both of which can negatively impact recovery if not properly controlled.
Prompt diagnostic and therapeutic interventions, such as coronary angiography and revascularization techniques, are crucial for addressing the underlying causes of cardiac arrest. These procedures not only confirm the presence of arterial obstructions but also allow for immediate treatment to restore blood flow. By integrating these targeted strategies, healthcare providers can enhance patient stability and improve long-term outcomes following cardiac arrest events, as outlined in this comprehensive guide to heart health and cardiac care.
Emphasis on Team-Based Approach and Communication
Coordinated teamwork remains a cornerstone of successful resuscitation, as highlighted in the latest ACLS guidelines. Establishing a structured hierarchy with clearly defined roles ensures that all resuscitation members work in harmony, maximizing the efficiency of interventions. The role of a leader—entrusted with strategizing and adapting interventions according to situational needs—proves vital, as this individual guides the team’s actions while ensuring adherence to protocols.
To achieve optimal outcomes, communication must be precise and effective. The guidelines recommend employing clear feedback techniques to avoid misunderstandings and ensure task completion. This method involves confirming receipt of instructions, thereby reinforcing accountability and enhancing situational awareness among team members. By actively engaging all participants, the team can execute complex interventions smoothly, reducing the likelihood of errors during high-stakes scenarios.
Reflective practices following resuscitation offer a platform for collective learning and emotional support. Post-event discussions allow teams to analyze their performance, celebrate successes, and identify areas needing refinement. This approach not only sharpens technical skills but also addresses the emotional impact of resuscitation on caregivers, fostering a culture of resilience and continuous improvement.
The 2025 ACLS guidelines represent a significant step forward in the management of cardiac arrest and other life-threatening cardiovascular emergencies. By staying current with these evidence-based recommendations, healthcare professionals can provide the highest quality care to their patients and improve outcomes. If you’re looking to obtain or renew your ACLS certification, we invite you to explore our comprehensive online courses at Affordable ACLS – purchase your certification or recertification course today and join us in our mission to save lives through accessible, high-quality education.

