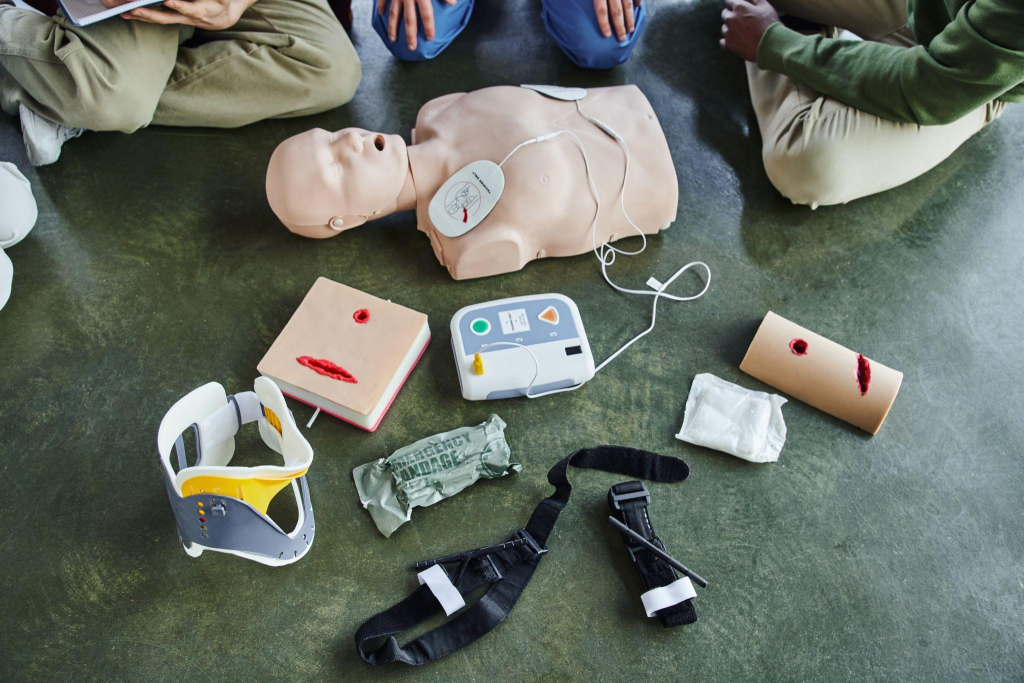
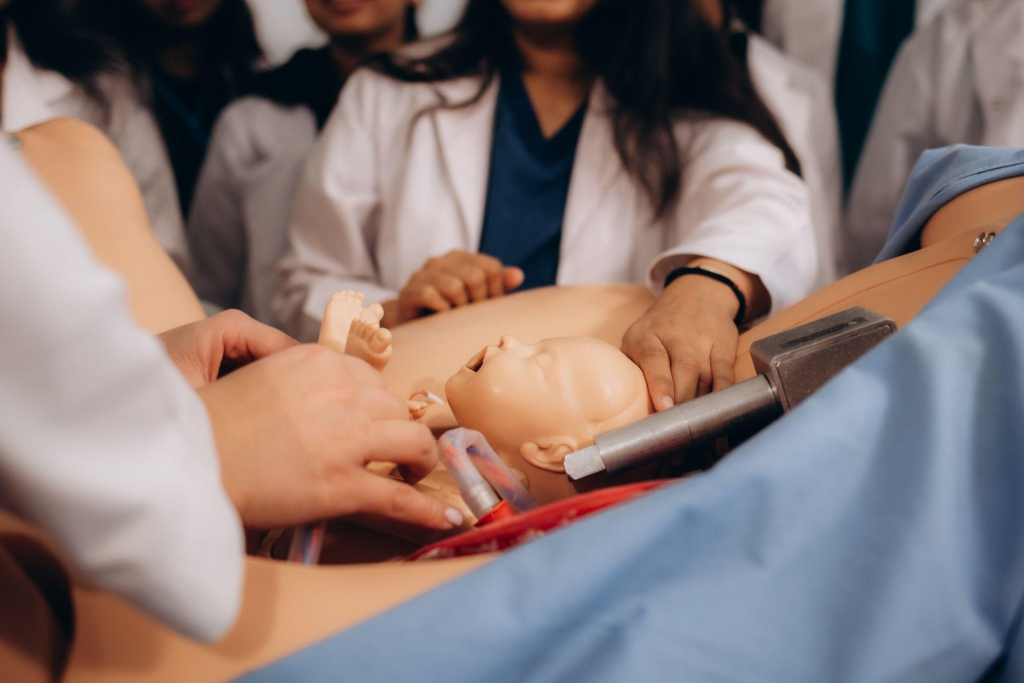
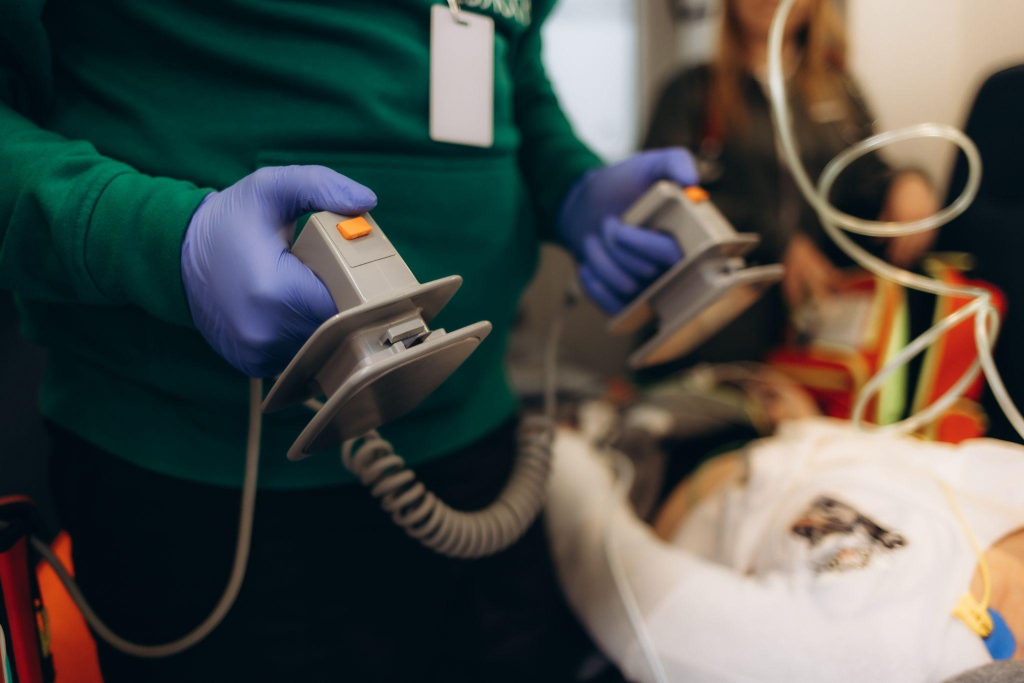
Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) is a critical component of emergency medical care, particularly in cases of cardiac arrest or other life-threatening cardiovascular emergencies. However, delivering effective ACLS training and services in remote and rural settings presents unique challenges that require innovative solutions and tailored approaches.
The vast distances, limited medical resources, and unique circumstances of rural areas create barriers to timely and effective emergency response. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial to ensure that residents of remote communities have access to the same level of care as their urban counterparts.
By identifying the specific challenges faced by healthcare professionals in rural settings and developing targeted strategies to address them, we can significantly improve the quality and accessibility of ACLS services in these areas. This article will explore the key aspects of implementing ACLS in remote and rural settings, focusing on overcoming the challenges posed by geographical, logistical, and resource limitations.
What is ACLS in Remote and Rural Settings?
ACLS in remote and rural settings refers to the application of Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support protocols in areas with limited medical infrastructure and resources. These settings often face unique challenges such as longer emergency response times, limited access to specialized training, and the need for innovative solutions to deliver effective healthcare.
In rural communities, access to life-saving interventions like ACLS can be a critical challenge. The vast distances, limited medical resources, and unique circumstances of rural areas create barriers to timely and effective emergency response. Implementing ACLS in these settings requires a multifaceted approach involving training, resource allocation, technological innovation, and policy development.
One of the primary challenges in remote regions is the lack of adequate healthcare infrastructure and facilities. Investing in the establishment of primary health centers equipped with necessary medical equipment and technologies is essential. Additionally, ensuring a steady supply of essential medicines and vaccines is crucial to provide quality healthcare in these areas.
Another significant challenge is the shortage of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and specialists. Developing strategies for recruiting and retaining healthcare professionals in remote areas, such as improved salary packages, career development opportunities, and subsidized housing, can help overcome this challenge. Moreover, tailoring healthcare education and training programs to the specific needs of rural areas is vital to promote the development of a workforce prepared to serve in these regions.
Telemedicine and telehealth initiatives can play a pivotal role in enhancing rural healthcare by enabling remote consultations and support from specialists. Implementing these technologies involves setting up video consultation centers in primary health centers or utilizing mobile applications to connect patients with healthcare providers. By leveraging telemedicine, rural populations can receive timely medical advice and consultations without the need for long-distance travel.
Strengthening transportation and communication networks is crucial to facilitate timely access to healthcare services and enable effective communication between healthcare providers and patients. Investing in improving transportation infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and air ambulances, along with expanding mobile phone coverage and internet connectivity, can significantly enhance emergency response capabilities in rural areas.
Lack of awareness and education about healthcare is another challenge faced by rural populations. Developing targeted educational campaigns and awareness programs that focus on promoting preventive healthcare practices, raising awareness about common diseases and their symptoms, and educating the population about the importance of regular check-ups and vaccinations is essential. By empowering rural communities with comprehensive healthcare knowledge, they can take proactive measures to prevent diseases and seek timely medical help when needed.
Enhancing rural healthcare requires active community participation and collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies, healthcare providers, community leaders, and non-profit organizations. Encouraging community involvement in healthcare decision-making processes, establishing health committees, and involving local healthcare providers in policy discussions ensures that the solutions developed are tailored to the unique needs of each rural region.
In conclusion, overcoming the challenges of delivering ACLS in remote and rural settings requires a combination of education, collaboration, and resourcefulness. By acknowledging the unique circumstances of rural areas and tailoring training and resources to address these challenges, communities can enhance their ability to respond effectively to emergencies. Fostering a culture of preparedness and equipping individuals with the tools they need to be the first line of defense when every second counts is paramount to success. Through strategic efforts and community engagement, rural areas can bridge the accessibility gap and ensure that life-saving interventions like ACLS are within reach for all residents.
How to Implement ACLS in Remote Settings
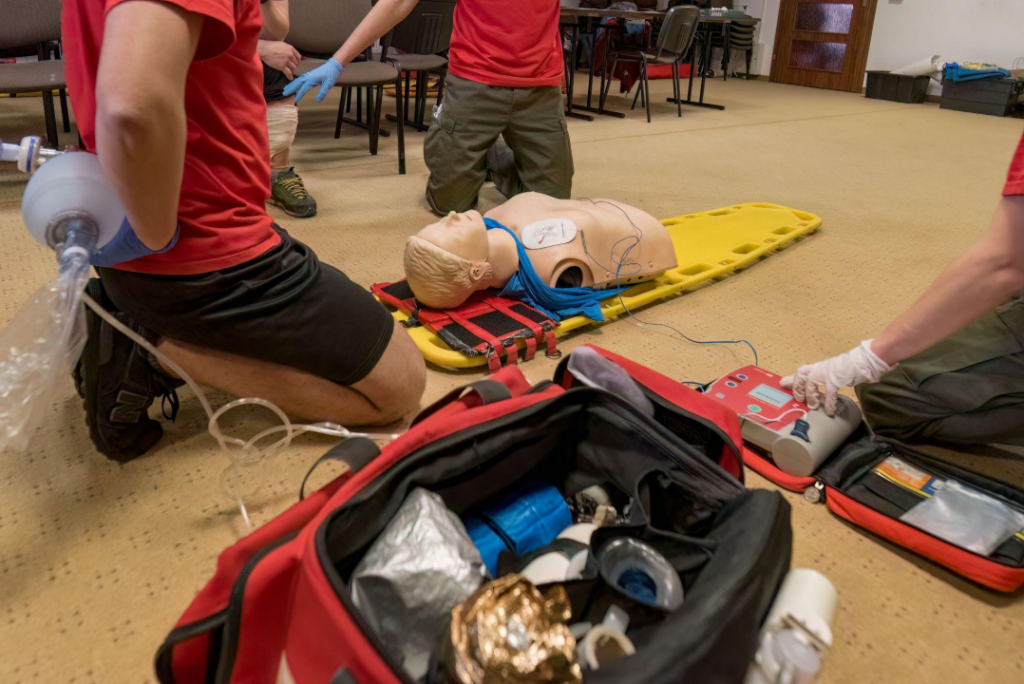
Implementing ACLS in remote settings requires a nuanced understanding of the distinct challenges these areas face. The process begins with crafting strategic plans that directly address the specific needs and constraints of rural communities. These plans should focus on optimizing available resources while pinpointing where support is lacking. By conducting comprehensive analyses, healthcare providers can determine the state of local medical infrastructure, capabilities of personnel, and equipment status, enabling well-informed decisions on resource distribution and training necessities.
Evaluating Local Capabilities and Infrastructure
An in-depth evaluation of local capabilities and infrastructure forms the foundation of a successful ACLS implementation strategy. This involves a detailed review of the healthcare facilities’ conditions, staff proficiency, and medical equipment availability. It is crucial to identify deficiencies in ACLS training and resource allocation to pinpoint where targeted improvements are necessary. For example, remote regions may face challenges such as outdated medical technology or insufficient numbers of trained personnel to administer ACLS protocols effectively. Addressing these deficiencies through focused initiatives can enhance emergency response outcomes.
Core Evaluation Components:
- Facilities: Inspect the adequacy and readiness of existing healthcare centers.
- Personnel: Gauge the skill levels and readiness of healthcare providers in ACLS protocols.
- Equipment: Review the presence and operational status of critical ACLS equipment, like defibrillators and emergency medication kits.
Facilitating Access to Advanced Training
After assessing local capabilities, the next step is to facilitate advanced training opportunities for healthcare providers in remote areas. Innovative online ACLS certification programs offer a flexible approach to enhancing practitioners’ competencies and keeping them informed about the latest ACLS guidelines. By promoting continuous professional development and encouraging practitioners to engage in ongoing education, remote communities can fortify their emergency response teams. This continuous learning is essential for maintaining high standards of care and ensuring healthcare providers are equipped to manage complex medical emergencies effectively.
Leveraging Telehealth Innovations
Telehealth innovations serve as a critical bridge in overcoming the physical barriers of distance, enhancing the delivery of ACLS in remote settings. By enabling remote consultations and expert guidance during emergencies, telehealth systems can significantly improve patient care outcomes. Additionally, telehealth platforms offer a robust avenue for continuous learning and updates on ACLS practices, ensuring healthcare providers remain current with medical advancements. Deploying comprehensive telehealth solutions can connect remote communities with urban medical centers, guaranteeing quality healthcare access irrespective of location.
Through strategic planning, advanced training facilitation, and the integration of telehealth innovations, ACLS can be adeptly implemented in remote settings. By addressing the specific challenges of geographical and resource constraints, healthcare providers can bolster their emergency response capabilities and extend life-saving interventions to underserved populations.
Step 1: Assess Local Needs and Resources
A comprehensive understanding of local healthcare environments is vital for adapting ACLS strategies in remote areas. Begin with a focused review of healthcare infrastructure, ensuring that facilities are equipped to manage emergency scenarios effectively. This involves examining both the physical condition of healthcare settings and their operational capabilities to handle high-stakes medical interventions.
Infrastructure and Personnel Assessment
Delve deeper into assessing the skills and readiness of healthcare personnel. Understanding the current capabilities and training levels of staff can pinpoint areas necessitating enhancement. This insight is crucial for implementing targeted educational initiatives that elevate the proficiency of medical teams in executing ACLS protocols.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Evaluate the operational efficiency and accessibility of medical facilities, ensuring they can serve as reliable emergency response hubs.
- Staff Proficiency: Analyze the training and experience levels of healthcare workers, focusing on their ability to deliver competent ACLS care.
Equipment Inventory and Resource Enhancement
Conduct a thorough examination of the available medical equipment, essential for effective ACLS delivery. Identifying gaps in resources—such as the availability of defibrillators and critical care tools—enables the formulation of strategic plans to enhance equipment readiness, possibly through partnerships or funding opportunities.
- Resource Inventory: Perform a detailed evaluation of existing medical equipment, noting any deficiencies or areas for improvement.
- Resource Augmentation: Identify and address shortages in equipment and personnel, facilitating timely interventions to strengthen local emergency healthcare infrastructure.
Enhancing Knowledge and Skills
Addressing knowledge gaps remains a key component in reinforcing ACLS capabilities. Utilizing remote learning platforms offers a flexible approach to supplementing local expertise, ensuring that healthcare providers have access to up-to-date ACLS protocols and practices. These educational resources are pivotal in preparing practitioners to respond effectively to emergencies, enhancing overall community resilience.
Step 2: Provide Access to Comprehensive Training
Enhancing the skills of healthcare providers in remote areas is essential for effective ACLS implementation. Online platforms offer a unique opportunity to deliver advanced training without geographical constraints. These courses allow healthcare professionals to refine their abilities and stay current with medical advancements, all while accommodating their demanding schedules.
Customizing Training for Practical Application
Training programs must be designed to address the specific conditions and challenges of rural healthcare environments. Utilizing modules that present realistic scenarios faced in remote settings ensures that practitioners gain practical insights. Such targeted learning equips them with confidence and competence to handle emergencies effectively.
Crucial Aspects of Customized Training:
- Realistic Simulations: Incorporating exercises that mimic actual emergencies common in rural areas to improve decision-making skills.
- Engaging Content: Interactive elements like quizzes and multimedia presentations enhance understanding and memory retention.
- Adaptive Scheduling: Providing courses that can be accessed anytime ensures learning continuity despite varied internet availability and work commitments.
Promoting Lifelong Learning
Keeping abreast of the latest ACLS protocols and innovations is vital for healthcare professionals. By fostering a culture of continuous education, practitioners remain well-informed about emerging medical practices and technologies. This commitment to ongoing learning not only improves individual capabilities but also strengthens the overall healthcare delivery system in remote communities.
- Frequent Updates: Platforms should consistently refresh content with the latest research and guideline modifications.
- Community Interaction: Creating spaces for discussion and knowledge exchange promotes a supportive and collaborative educational environment.
- Regular Re-certification: Encouraging periodic re-certification ensures that healthcare providers maintain high proficiency levels in their practice.
By prioritizing access to tailored and continuous training, healthcare providers in remote settings can deliver superior emergency care. This dedication to skill enhancement is fundamental in bridging the healthcare gap for rural populations.
Step 3: Establish Local Emergency Response Teams
Creating proficient local emergency response teams is crucial for ensuring timely interventions in rural settings where immediate advanced care may not be accessible. These teams, comprising trained volunteers and healthcare workers, are invaluable in initiating life-saving procedures swiftly, acting as a crucial link until more comprehensive medical assistance can be mobilized.
Training and Empowerment
The success of these teams depends on robust training programs that impart critical skills in emergency medical procedures. Training should incorporate practical exercises that reflect the specific challenges of rural environments, allowing team members to gain hands-on experience in handling real-world medical emergencies. This experiential learning not only boosts individual confidence but also enhances team dynamics, which is vital for coordinated emergency responses.
- Targeted Skill Development: Provide instruction in CPR techniques, AED operation, and basic trauma care suited to the local context.
- Interactive Workshops: Organize workshops that simulate emergency scenarios common in the area, emphasizing quick decision-making and teamwork.
- Regular Training Updates: Offer periodic training updates to ensure responders remain proficient and informed about the latest emergency care advancements.
Building a Cohesive Network
Establishing a well-integrated network of emergency responders within the community requires strategic planning and effective communication. These teams should work in tandem with local healthcare facilities and emergency services to create a seamless response mechanism. Developing clear pathways for communication and collaboration ensures all parties are synchronized during emergencies, maximizing the efficiency of response efforts.
- Efficient Communication Channels: Set up reliable communication systems that facilitate rapid information sharing between response teams, medical facilities, and emergency services.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Engage with local authorities and health organizations to secure resources and support for the teams.
- Community Involvement: Involve community leaders in planning and preparedness activities to build trust and encourage broader community participation.
By equipping local emergency response teams with the necessary skills and establishing a strong support network, remote communities can enhance their capacity to manage medical emergencies effectively. These teams not only provide crucial immediate care but also strengthen community resilience and foster a culture of proactive health management.
Step 4: Integrate Telehealth Solutions
Integrating telehealth solutions into rural healthcare systems transforms the accessibility and scope of medical care in remote settings. Telehealth platforms facilitate the delivery of healthcare services that overcome geographical barriers, allowing for a more comprehensive approach to patient care. These systems play a crucial role in ensuring that healthcare providers can access necessary resources and expertise despite being in isolated locations.
Virtual Consultations and Expert Guidance
Telehealth systems provide a vital link between rural healthcare providers and a network of medical experts, enabling more informed clinical decisions. This connectivity ensures that healthcare workers in remote areas can consult with specialists for critical insights, thereby enhancing the precision and effectiveness of medical interventions.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Deploy platforms that support secure video communications and data exchange to link rural providers with specialists.
- Expert Access: Develop collaborations with specialty medical centers to create a readily accessible pool of experts for consultation.
- Collaborative Care: Use telehealth for joint patient management efforts, where specialists can contribute to care strategies and treatment recommendations.
Ongoing Education and Knowledge Sharing
Telehealth serves as a continuous learning platform, offering rural healthcare providers access to the latest medical education and developments. By facilitating regular updates and training through telehealth, practitioners can keep their skills and knowledge current, thus maintaining high standards of care.
- Digital Learning Sessions: Host live virtual events featuring updates on new medical protocols and healthcare innovations.
- Self-directed Learning Materials: Create interactive content available through telehealth for flexible learning opportunities.
- Professional Networking: Encourage participation in online discussion groups to promote the exchange of ideas and experiences among peers.
Advancing Healthcare Delivery
Through telehealth integration, healthcare delivery in remote regions becomes more dynamic and adaptive, reducing the limitations imposed by distance and resource scarcity. This approach not only improves immediate patient access to care but also builds a more robust and informed healthcare system, capable of delivering consistent, high-quality medical services in challenging environments. By leveraging telehealth, rural communities can achieve enhanced healthcare outcomes and a sustainable model for medical excellence in underserved areas.
Step 5: Ensure Availability of Essential Equipment
The effectiveness of ACLS in remote settings hinges on the critical availability of medical equipment. This involves more than just possessing the necessary tools—it requires a strategic approach to ensure equipment is operational and accessible when needed most. Collaborating with healthcare facilities to prioritize equipment management and resource allocation is key to overcoming logistical challenges. By focusing on robust planning and efficient resource distribution, facilities can maintain readiness for emergencies.
Strategic Equipment Management
To optimize equipment availability, facilities must implement a structured approach to resource management. This includes establishing proactive measures to maintain equipment functionality and addressing potential shortages before they affect service delivery. By devising detailed plans for equipment procurement and upkeep, healthcare facilities can better support their emergency response capabilities.
- Regular Equipment Audits: Conduct systematic evaluations to monitor the condition and availability of equipment, ensuring readiness for emergencies.
- Maintenance Frameworks: Implement comprehensive maintenance schedules to reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of critical medical tools.
- Resource Prioritization: Allocate resources strategically to areas where they will have the most significant impact, considering the specific emergency care needs of the community.
Community and Partnership Engagement
In remote areas, enhancing medical infrastructure often requires innovative resource acquisition strategies. Engaging the local community and forming strategic alliances with external partners can significantly bolster efforts to provide essential medical equipment. By cultivating a cooperative environment, communities can actively contribute to strengthening their healthcare systems.
- Local Collaboration Efforts: Initiate community-driven projects to support the acquisition and sustainability of medical resources, fostering a sense of shared responsibility.
- Strategic Alliances: Develop partnerships with non-profit organizations, governmental bodies, and private entities to access funding and equipment donations.
- Awareness and Advocacy: Increase public awareness about the importance of medical equipment in emergency care, encouraging community involvement in resource mobilization efforts.
By ensuring the robust availability and functionality of essential medical equipment, healthcare providers in remote settings can significantly enhance their ability to deliver effective ACLS interventions. This strategic approach not only improves patient outcomes but also builds a resilient healthcare infrastructure capable of meeting the unique challenges of rural environments.
Step 6: Promote Community Awareness and Involvement
Strengthening the fabric of emergency medical response in rural areas hinges on active community participation. By integrating local residents into preparedness initiatives, healthcare systems can develop a resilient support network that enhances overall emergency response capability. Outreach programs aimed at demonstrating the critical role of ACLS can motivate individuals to take a proactive stance towards emergency readiness.
Tailored Educational Programs
Educational initiatives should be crafted to align with local cultural contexts, addressing specific challenges faced by the community. These programs should focus on practical training that empowers individuals with vital life-saving knowledge and skills. By providing hands-on learning experiences, communities can become more adept at responding to emergencies.
- Interactive Learning Sessions: Implement sessions that involve hands-on practice of emergency procedures, ensuring participants gain confidence and competence.
- Community Skill-Building Events: Host events that focus on skill enhancement, using real-life scenarios to illustrate the application of ACLS principles.
- Youth Engagement Initiatives: Encourage participation from younger community members through school programs that introduce fundamental emergency response concepts.
Cultivating a Network of Preparedness
Effective emergency preparedness requires a collaborative approach, where healthcare providers and community members engage in continuous dialogue. By establishing partnerships and communication channels, healthcare systems can maintain an active presence, reinforcing the importance of readiness and collective action in emergencies.
- Joint Community-Healthcare Events: Organize collaborative events that bring together healthcare professionals and community members to discuss emergency strategies and share resources.
- Responsive Feedback Systems: Develop mechanisms to capture community feedback on healthcare programs, ensuring they adapt to evolving local needs.
- Strategic Alliances with Local Groups: Forge partnerships with community organizations to expand the reach of ACLS awareness, leveraging existing networks for broader impact.
By fostering community awareness and involvement, rural healthcare systems can harness the strengths of local populations to enhance emergency preparedness and response efforts. This inclusive approach not only bolsters the efficacy of ACLS interventions but also empowers communities to take an active role in maintaining their health and safety.
Implementing ACLS in remote settings requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the unique challenges faced by rural communities. By focusing on strategic planning, advanced training, and innovative solutions like telehealth, healthcare providers can significantly enhance their emergency response capabilities. We invite you to explore our online certification and recertification courses designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to deliver life-saving interventions in any setting—purchase your course today and join us in our mission to improve healthcare access and outcomes in remote areas.